Cafe Au Lait Stains In Children: Need To Worry?

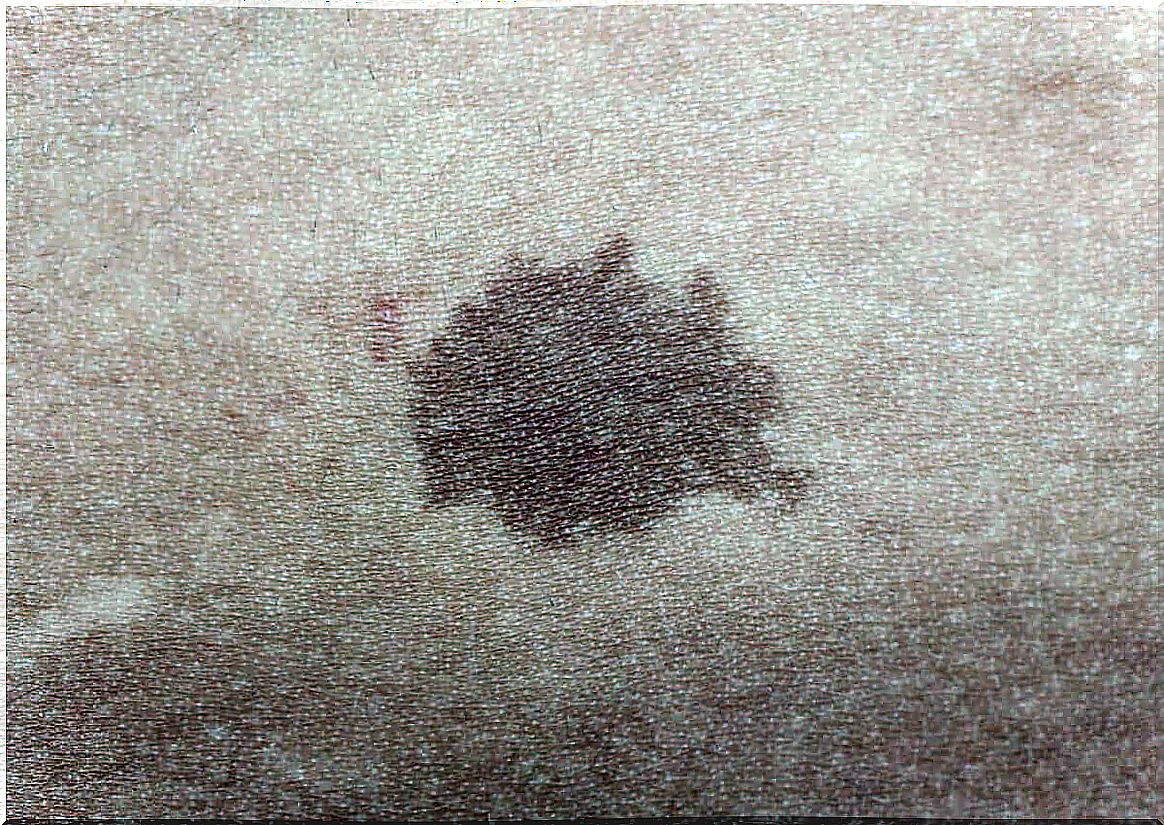
Café-au-lait spots are light brown, homogeneous-appearing macules on the skin that occur in 25% of children. The amount or size that can be observed usually varies. In addition, they are harmless and normal, but their importance is that it could be considered one of the manifestations of type I neurofibromatosis .
What are café au lait spots?
This type of manifestation on the skin is blemishes without relief, hyperpigmented that appear as a focused area of increase in the generation of melanin, skin pigment.
As the child grows, the café-au-lait spots may grow in tandem. They can even be found anywhere on the body, with a greater preference for the trunk and extremities.
They are observed more frequently in black people, which does not exclude that there are records of presence in people with a lighter complexion.
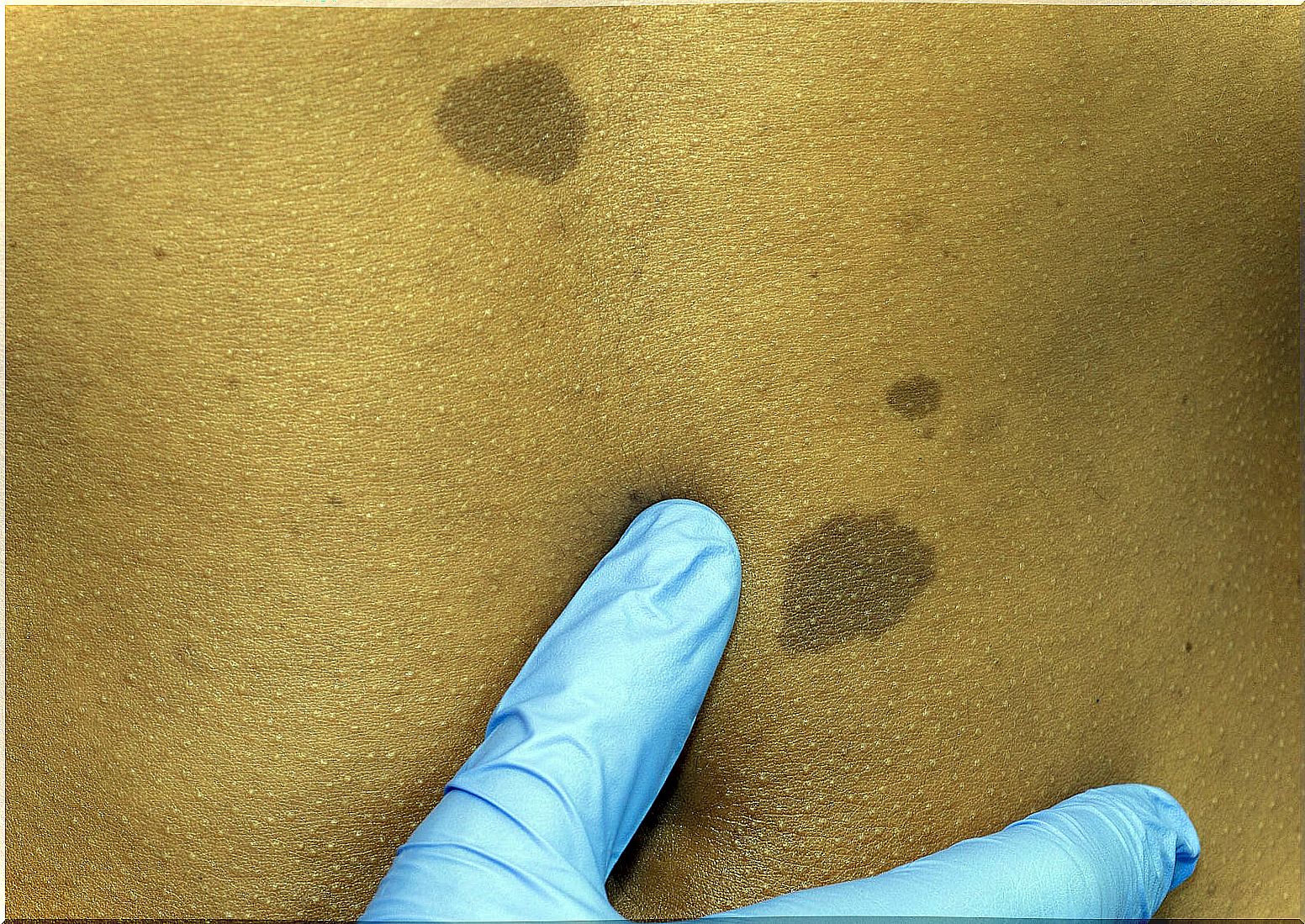
The size of each of them can vary from 2 mm to more than 20 cm in diameter. In turn, they tend to be lighter at the beginning of their appearance and intensify their tonality over time.
Why do café au lait spots originate?
They can be congenital or develop over time. Café au lait spots are associated with different types of genetic syndromes; some of them include the following:
- Neurofibromatosis I.
- Neurofibromatosis II.
- McCune-Albright syndrome.
- Syndorm of Legius.
- Tuberous sclerosis.
In those children in whom there are more than 6 café-au-lait spots greater than 5 mm before the puberty stage, or greater than 15 mm after puberty, the cause should be suspected to be Neurofibromatosis I.
Neurofibromatosis I or von Reckinhausen disease
Neurofibromatosis I is the most common of all neurofibromatosis. It is estimated that it affects around 1 in 3,500 births.
It has its genetic origin due to a mutation of the NF1 gene , with an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern. According to a review by the Spanish Association of Pediatrics , the presence of café-au-lait spots is one of the criteria to establish its diagnosis along with two of the following:
- Plexiform neurofibroma.
- Ephelides in the axillary or inguinal area.
- 6 or more coffee with milk stains.
- Optic glioma.
- A distinctive bone lesion.
- 2 or more Lisch nodules.
- A first-degree relative with the above criteria.
Learning disability, attention deficit disorder, shorter-than-average height, precocious puberty, high blood pressure, scoliosis, headache, and larger-than-normal head size may also be evidenced.
The symptoms of neurofibromatosis can be mild in some children, but severe in others. In turn, there may be different characteristics of the disease among members of the same family.
Can café au lait spots be prevented?
Regarding the prevention of the appearance of this type of benign and pigmented lesions, there is no recommendation. This is because they are not like nevi, a product of constant exposure to the sun’s rays.
On the contrary, some are congenital or arise in the first days of life, a period in which babies should not receive direct sunlight.
Treating café au lait spots
Café-au-lait macules do not undergo malignant transformation over time. Consequently, no treatment is required for them, unless they generate an aesthetic discomfort in the sufferer.

The laser as a therapeutic option
In those cases in which it is considered to start a therapy, laser treatment is the first option. This can generate a partial lightening of the spot, but a recurrence is not ruled out.
This type of treatment requires several sessions and the risks that exist are the same as in any laser procedure:
- Transient or permanent hyperpigmentation.
- Hypopigmentation.
- Sensitivity of the skin.
- Residual scars.
The sessions to perform this procedure usually last a few minutes and, in most cases, it is usually expected between 6 and 8 weeks to perform the next session.
When should a pediatrician be consulted?
In the case of presenting brown spots, a medical consultation should be scheduled so that the specialist can determine if they are isolated lesions or are part of a genetic syndrome. Thus, the doctor will conduct the interrogation according to the background. In turn, it will request the necessary and corresponding studies to rule out all possible differential diagnoses.
If it is a small number of café-au-lait spots, only the pertinent control of its evolution (size and number) will be carried out and parents will be instructed to be alert to any new symptoms related to some of the diseases that manifest them. .