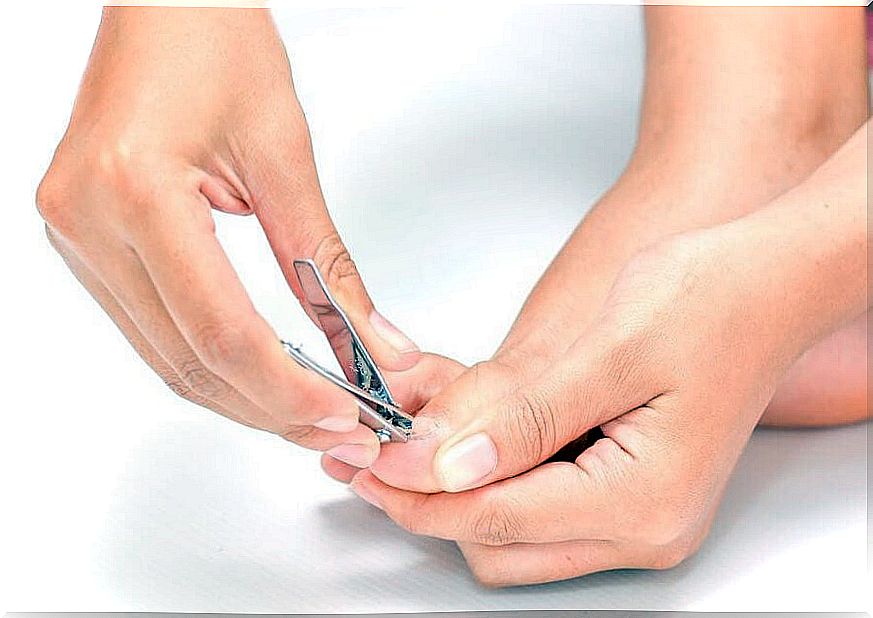
Paronychia In Children: Symptoms, Causes And Treatment
Paronychia in children is one of the most common infections of the hand, although it can also occur on the toes. Although they are not malignant lesions, they are usually annoying due to the intense pain they cause. Therefore, you must act quickly to avoid the evolution of the picture, and, therefore, the increase in the disease.
What is paronychia in children?
Paronychia is an infection of the lateral and proximal folds of the toenails and fingernails. In turn, the tissues surrounding the nail and those bordering the root are included in this pathology. It is a pathology that occurs with greater prevalence in women.
Causes of paronychia
Paronychia can be triggered spontaneously or after having generated trauma or some manipulation. It is produced by the breakdown of the protective barrier that exists between the nail fold and the nail. Consequently, this disruption is exploited by bacteria and predisposes the area to infection.
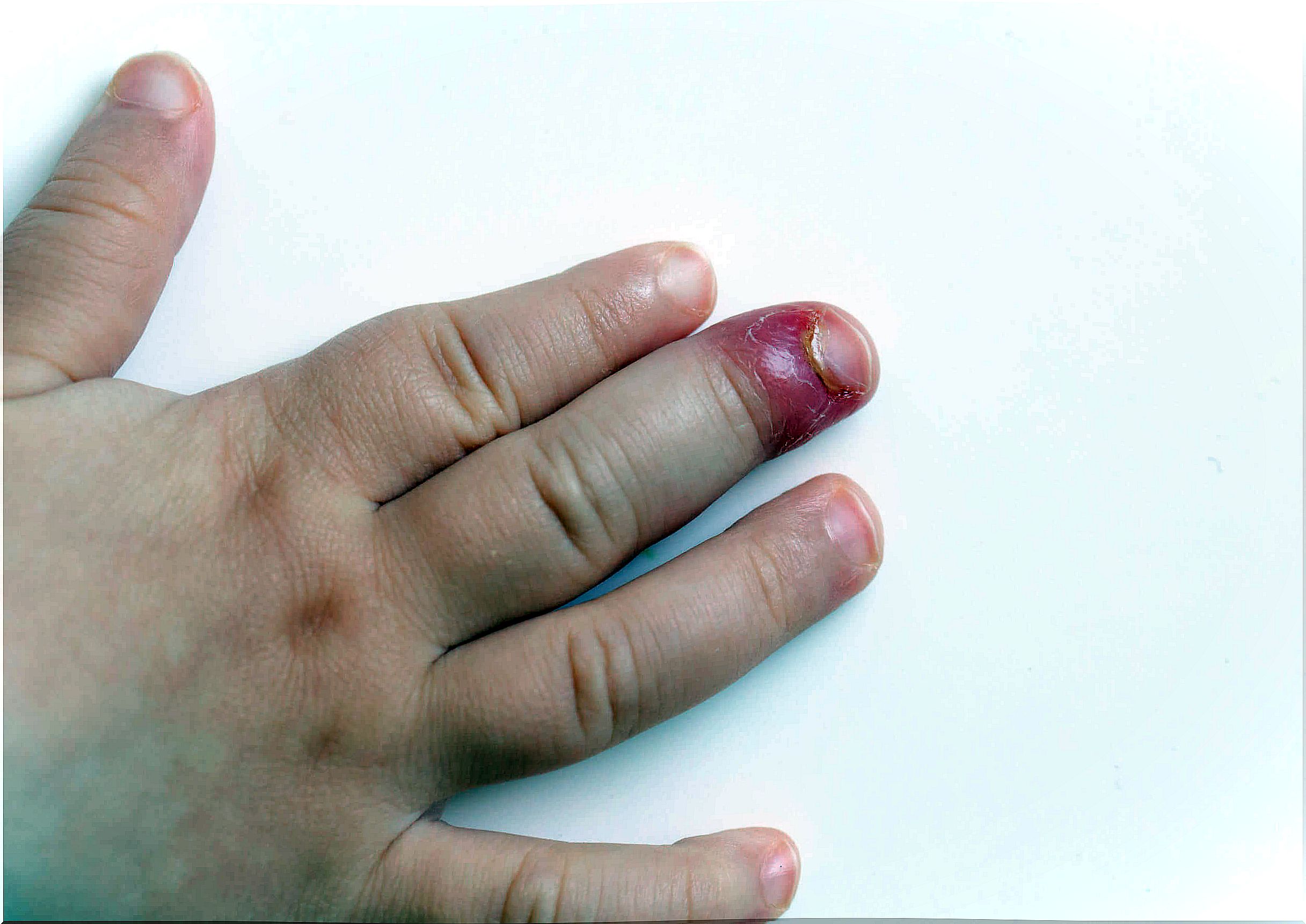
However, it can be generated by contact with certain irritants or allergens. In the event that the pathology is induced by any medication, the clinical manifestations will be reflected in all the nails. Whereas when the picture is sharp it will only be limited to one.
Classifications of Paronychia
Nail fold disease can admit different classifications. According to the clinical presentation of paronychia, the American Family Physician distinguishes the following meanings:
- Acute Paronychia : Symptoms tend to last a maximum of six weeks. In addition, it is usually caused by bacteria and causes pain and purulent discharge.
- Chronic Paronychia : It is developed by chemical or mechanical agents, or in rare cases, by the Candida fungus . It is presented with a greater predisposition in certain trades (waiter, dishwasher and housekeeper), immune system disorders and with certain drugs.
In addition to this classification, there is also a differentiation regarding its origin, which can be bacterial, viral or fungal.
Clinical manifestations of paronychia in children
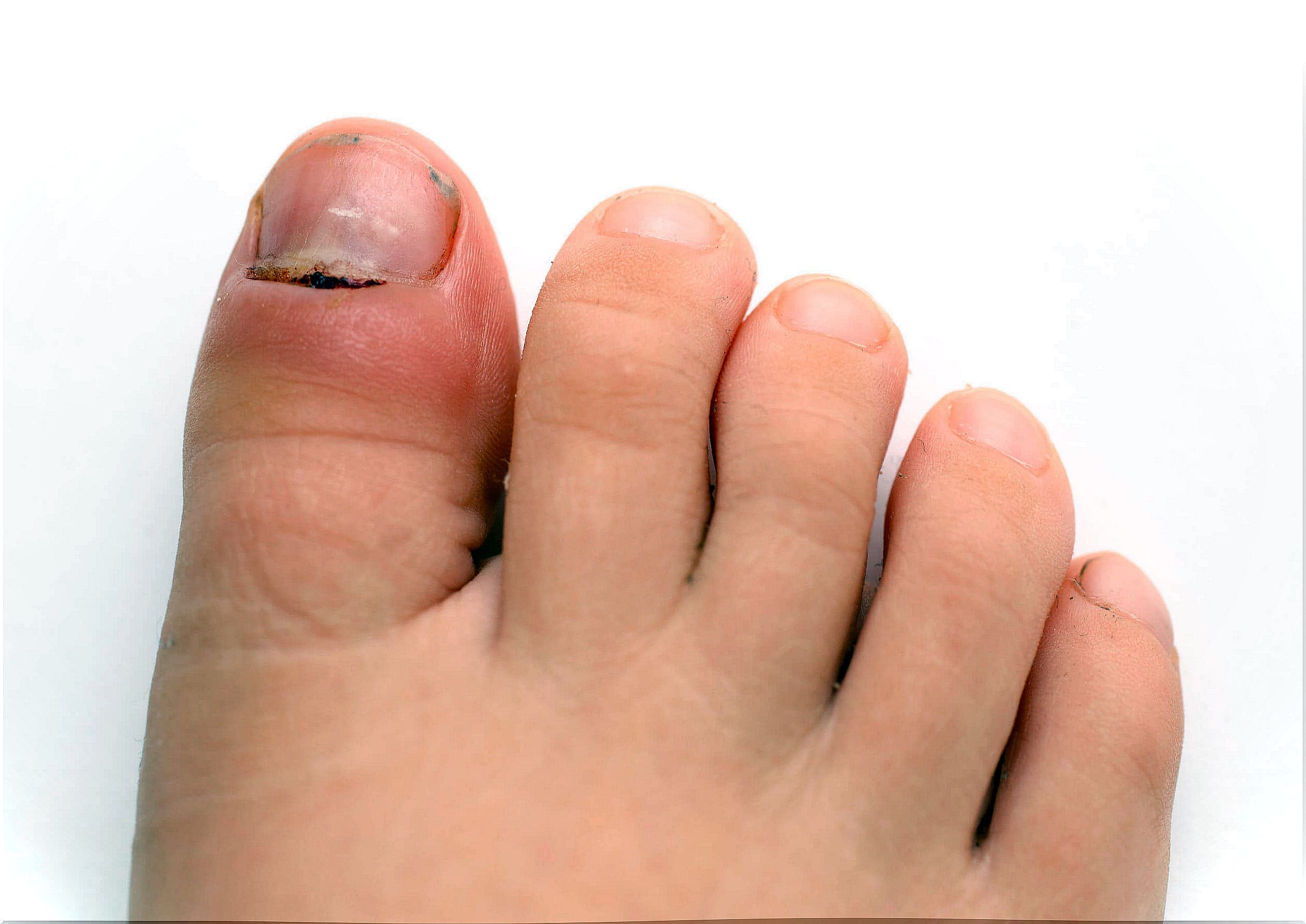
Paronychia is an acute or chronic inflammatory process that causes painful redness and edema in the lateral folds of the nails. Even the child’s pain is the main symptom that leads the father to consult the doctor.
It is diagnosed with the clinical presentation of the infection. Consequently, he presents an erythematous, tender and inflamed nail ridge and the nail thick and discolored.
Other common findings of paronychia can be nail dystrophy, retraction of the proximal nail fold, and loss of the cuticle. In fact, the presence of an abscess is not always obvious.
Treatment options for paronychia in children
General preventive measures are the basis of the treatment of paronychia in children. These help prevent and work synergistically with other active measures to speed up healing times and minimize potential recurrences.
General measures
The primary goal is to try to avoid aggravating factors and decrease added injury by reducing nail manipulation.
- Avoid exposure to humid environments and contact irritants, such as detergents and soaps.
- The affected area should be kept dry and the application of moisturizer after hand washing is recommended .
- Avoid manipulation of the nails (manicuring, sucking the fingers or trying to make an incision and drain the injury).
- Choose the right footwear to avoid unnecessary damage to the nail.
Medical management of paronychia in children
Currently, the first-line topical treatment is corticosterides, although in the past the mainstay of therapy was antifungal. However, the use of antifungal agents is resorted to when there is an associated fungal infection.
Topical 0.1% tacrolimus is another good option for chronic paronychia. Studies even reveal the greater efficacy it presents with respect to the use of topical corticosteroids. In children in whom topical treatment fails or in more severe cases, oral antibiotics should be used.
Surgical management
Surgical intervention is only indicated in those recalcitrant cases of chronic paronychia that do not respond to medical management and the correct use of general measures.
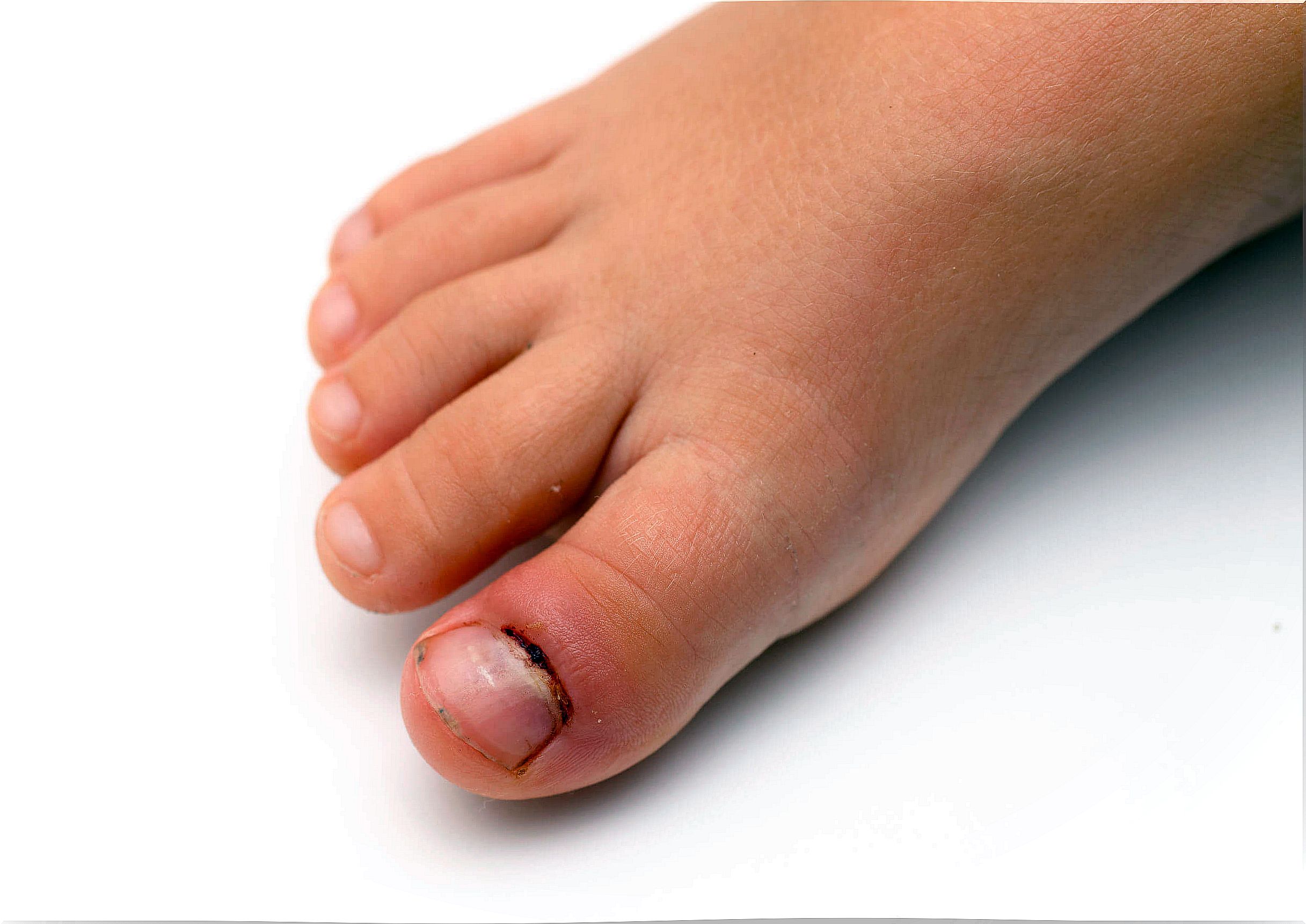
The inflamed tissue is removed, which contributes to the effective penetration of topical drugs and the correct regeneration of the cuticle. Also, if there is an abscess, the infection will require drainage.
The importance of medical consultation
Today, there are countless homemade recipes that are shared between people. However, this type of self-medication is not recommended in paronychia.
There is a risk of generating complications or superinfections due to contact with products that are not appropriate for medicinal use. Therefore, at the first sign or symptom, you should go to the doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.